Small Home Plans With Vaulted Ceilings: Expanding Space and Style
Small home living embraces efficiency and clever design to maximize limited square footage. Among the architectural strategies employed to achieve a sense of greater spaciousness, vaulted ceilings stand out as a particularly effective and aesthetically pleasing option. Vaulted ceilings, characterized by their upward sloping surfaces that meet at a central ridge, can transform a cramped interior into a bright, airy, and visually expansive environment. Integrating vaulted ceilings into small home plans requires careful consideration of structural integrity, insulation, energy efficiency, and overall design coherence. However, the benefits of incorporating this feature often outweigh the challenges, leading to a more comfortable and appealing living space.
This article explores the various aspects of small home plans that incorporate vaulted ceilings, examining the different types of vaulted ceilings suitable for smaller spaces, the advantages and disadvantages of each, and the design considerations crucial for successful implementation. It delves into the impact of vaulted ceilings on lighting, acoustics, and heating/cooling, and discusses strategies to mitigate any potential drawbacks. By understanding the nuances of vaulted ceiling design, homeowners and architects can create small homes that feel significantly larger and more luxurious than their actual footprint suggests.
Types of Vaulted Ceilings Suitable for Small Homes
The term "vaulted ceiling" encompasses a range of designs, each with its unique aesthetic and structural characteristics. Choosing the right type of vaulted ceiling for a small home is essential to achieve the desired effect without overwhelming the space or compromising functionality. Several types are particularly well-suited for smaller floor plans:
Cathedral Ceiling: This is perhaps the most recognizable type of vaulted ceiling, featuring two equally sloped sides that rise to a central peak. Cathedral ceilings create a dramatic sense of height and openness, making them ideal for living rooms or great rooms in small homes. The symmetrical design lends itself well to modern and traditional styles alike. However, cathedral ceilings require careful insulation to prevent heat loss in colder climates and may necessitate additional structural support depending on the roof's span.
Shed Ceiling: A shed ceiling, also known as a single-slope or lean-to ceiling, features a single sloping surface that rises from one wall to the opposite wall. This type of vaulted ceiling is simpler and more cost-effective to construct than a cathedral ceiling. Shed ceilings are often used in contemporary and minimalist designs, and they can be oriented to maximize natural light from strategically placed windows along the higher wall. The single slope allows for efficient water runoff from the roof.
Gable Ceiling: Similar to a cathedral ceiling, a gable ceiling follows the roofline but typically only vaults over a portion of the room. This allows for a defined attic space or storage above the lower ceiling area. Gable ceilings offer a compromise between the dramatic height of a full cathedral ceiling and the practicality of a traditional flat ceiling. They are well-suited for bedrooms or dining areas in small homes, providing a sense of spaciousness without sacrificing storage opportunities.
Tray Ceiling: While not a true vault in the strictest sense, a tray ceiling features a recessed or inverted portion in the center of the ceiling, creating the illusion of height. This design is subtler than a full vault and can be incorporated into almost any room, regardless of its size. Tray ceilings are relatively easy to construct and can be enhanced with decorative moldings or recessed lighting to add visual interest. They serve as an excellent compromise when a full vaulted ceiling is not feasible or desired.
Arched Ceiling: This type of vaulted ceiling features a curved shape, adding a touch of elegance and sophistication to a small home. Arched ceilings can be implemented in various forms, from a gentle curve spanning the entire width of the room to a more pronounced arch over a specific area. They are particularly well-suited for Mediterranean or Spanish-style homes. The curved shape can also help to diffuse sound, improving the acoustics of the space.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vaulted Ceilings in Small Homes
The incorporation of vaulted ceilings into small home designs presents several advantages, but also certain drawbacks that need careful consideration. Weighing these pros and cons is crucial for making informed decisions about whether a vaulted ceiling is the right choice for a particular project.
Advantages:
Enhanced Sense of Spaciousness: The most significant advantage of vaulted ceilings is their ability to create a feeling of greater volume and openness, making a small home feel much larger than its actual square footage. The increased vertical space draws the eye upward, creating a more airy and less confined atmosphere.
Increased Natural Light: Vaulted ceilings often allow for the incorporation of larger windows or skylights, maximizing the amount of natural light entering the home. This not only brightens the interior but also reduces the need for artificial lighting, contributing to energy savings.
Improved Aesthetics: Vaulted ceilings add architectural interest and visual appeal to a small home. They can transform a plain and unremarkable space into a more dynamic and stylish environment, enhancing the overall aesthetic value of the property.
Improved Air Circulation: The increased height of vaulted ceilings can facilitate better air circulation within the home. Warm air naturally rises, creating a more even temperature distribution and reducing the likelihood of stagnant air pockets.
Disadvantages:
Higher Construction Costs: Vaulted ceilings typically require more complex framing and insulation than standard flat ceilings, resulting in higher construction costs. The need for specialized labor and materials can further increase expenses.
Increased Heating and Cooling Costs: Due to the larger volume of air to be heated or cooled, vaulted ceilings can potentially lead to higher energy bills. Inadequate insulation can exacerbate this problem, particularly in extreme climates. Proper insulation and ventilation strategies are essential to mitigate these costs.
Acoustic Challenges: Vaulted ceilings can create echo and reverberation problems if not properly addressed. The large, hard surfaces reflect sound waves, leading to a less comfortable acoustic environment. Using sound-absorbing materials such as carpets, curtains, and upholstered furniture can help to minimize these issues.
Maintenance Difficulties: Reaching high ceilings for cleaning or repairs can be challenging and may require specialized equipment or professional assistance. Tasks such as changing light bulbs or painting can become more complex and time-consuming.
Design Considerations for Small Home Plans with Vaulted Ceilings
Successfully integrating vaulted ceilings into small home plans requires careful attention to several key design considerations. These factors influence the overall aesthetic, functionality, and efficiency of the space.
Scale and Proportion: The height and slope of the vaulted ceiling should be proportional to the size of the room. An excessively high or steeply sloped ceiling can overwhelm a small space, while a ceiling that is too low or subtly angled may not achieve the desired effect. Careful consideration of the room's dimensions and the overall architectural style is crucial.
Structural Integrity: Vaulted ceilings require a robust structural framework to support the roof load and resist wind and seismic forces. Consulting with a structural engineer is essential to ensure that the design meets all applicable building codes and safety standards. The engineer can assess the load-bearing capacity of the walls and foundation and recommend appropriate framing techniques.
Insulation: Adequate insulation is critical for minimizing heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. Spray foam insulation, rigid foam insulation, and high-density fiberglass batts are effective options for insulating vaulted ceilings. Proper ventilation is also important to prevent moisture buildup and condensation, which can lead to mold growth and structural damage. Consider using a combination of insulation types and ventilation strategies to achieve optimal energy efficiency.
Lighting: Vaulted ceilings offer opportunities for creative lighting design. Recessed lighting, pendant lights, and chandeliers can be used to illuminate the space and add visual interest. Natural light can be maximized through the use of skylights or large windows. Consider the placement of lighting fixtures to avoid glare and shadows, and choose energy-efficient LED bulbs to reduce energy consumption.
Acoustics: As mentioned earlier, vaulted ceilings can create acoustic challenges. Incorporating sound-absorbing materials such as carpets, curtains, and upholstered furniture can help to minimize echo and reverberation. Acoustic panels can also be installed on the walls or ceiling to improve sound quality. Consider the intended use of the room when selecting acoustic treatments, and choose materials that complement the overall design aesthetic.
Window Placement: Strategically placed windows can maximize natural light and create a connection to the outdoors. Tall windows that follow the slope of the ceiling can visually expand the space and offer panoramic views. Skylights are another excellent option for bringing natural light into a vaulted ceiling. Consider the orientation of the windows to minimize glare and heat gain, particularly during the hottest hours of the day.
Material Selection: The materials used for the vaulted ceiling can significantly impact the overall aesthetic of the space. Wood beams add warmth and character to a vaulted ceiling, while painted drywall creates a clean and modern look. Consider the architectural style of the home and choose materials that complement the overall design. Pay attention to the texture and color of the materials, as these factors can affect the perceived size and warmth of the room.
By carefully considering these design factors, homeowners and architects can create small home plans with vaulted ceilings that are both beautiful and functional. The key is to balance aesthetic appeal with practicality, ensuring that the vaulted ceiling enhances the living space without compromising energy efficiency or structural integrity.

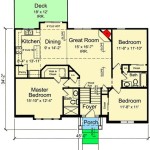
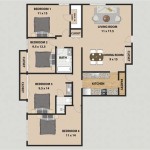
Small House Plan With Vaulted Ceiling All Bedroom Windows Directed In The Same Direction Floor Plans Building

Small House Plans Floor Modern Farmhouse

Small House Plan Ch192 With Vaulted Ceiling Home Design Four Bedrooms

Cathedral Ceiling House Plans Small W High Ceilings

Rustic House Plans Our 10 Most Popular Home

Affordable Home Ch102 With Vaulted Ceiling To Small Lot House Plan

Cathedral Ceiling House Plans Small W High Ceilings

Rustic House Plans Our 10 Most Popular Home

Plan 22139sl Adorable Tiny Home With Vaulted Ceiling House Plans Small Floor

Affordable Small Home 1 Bed 5 Bath 872 Sq Ft Plan 141 1324