Understanding Floor Plans: A Guide to Visualizing Your Home
Floor plans are scaled diagrams that depict the layout of a building, room, or property from a bird's-eye view. They are fundamental tools used in architecture, interior design, real estate, and construction. Understanding how to read and interpret floor plans is crucial for anyone involved in these fields, as well as for homeowners planning renovations, furnishing a new space, or simply understanding their property's structure.
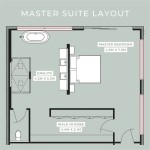
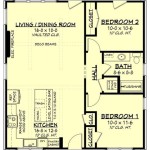
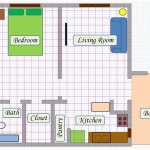
A floor plan typically shows walls, doors, windows, stairs, and fixed installations such as bathroom fixtures, kitchen cabinets, and appliances. They often include dimensions, indicating the size of rooms and the overall building footprint. More detailed floor plans may also include information about electrical outlets, lighting fixtures, and plumbing locations. Symbols and abbreviations are used to represent different elements, and a legend is often provided to explain these symbols.
The primary purpose of a floor plan is to provide a clear and concise representation of the spatial relationships within a building. This allows architects and designers to plan and visualize the flow of space, the placement of furniture, and the overall functionality of the design. For homeowners, floor plans offer a valuable tool for understanding the dimensions and layout of their property, which can be helpful for planning renovations, decorating, and even selling their home.
Key Element 1: Reading and Interpreting Floor Plan Symbols
One of the first steps in understanding floor plans is learning to recognize and interpret the symbols used to represent different elements. These symbols are standardized across the industry, though slight variations may occur depending on the specific architect or drafting software used. A typical floor plan symbol set will include representations for walls, doors, windows, stairs, fixtures, and appliances.
Walls are usually represented by thick lines outlining the perimeter of rooms and defining the boundaries of the building. The thickness of the line may vary depending on the type of wall, with thicker lines often indicating load-bearing walls. Doors are depicted as an arc indicating the swing direction and a straight line representing the door itself. Windows are typically shown as two or three parallel lines within the wall, sometimes with a break in the outer line to indicate the window frame.
Stairs are represented by a series of lines indicating the risers and treads, with an arrow typically pointing upwards to indicate the direction of ascent. Bathroom fixtures, such as toilets, sinks, and bathtubs, are shown as simplified representations of the actual objects. Kitchen appliances, like refrigerators, ovens, and dishwashers, are similarly depicted. It's common for the symbols to also include notations indicating specific models or manufacturers of appliances. A key or legend on the floor plan will explain each symbol used.
Understanding the dimensions provided on a floor plan is equally important. Dimensions are usually expressed in either imperial units (feet and inches) or metric units (meters and centimeters). They indicate the length and width of rooms, the overall building footprint, and the distances between various features. These measurements are essential for accurately visualizing the size of the space and planning the placement of furniture and other elements.
Pay close attention to the scale of the floor plan. The scale indicates the ratio between the dimensions on the drawing and the actual dimensions of the building. A common scale is 1/4 inch equals 1 foot (1/4" = 1'). This means that every quarter inch on the drawing represents one foot in the actual building. The scale is crucial for accurately interpreting the dimensions and understanding the relative size of different spaces.
Key Element 2: Using Floor Plans for Interior Design and Renovation
Floor plans are invaluable tools for interior design and renovation projects. They allow homeowners and designers to visualize the space, plan the layout of furniture, and identify potential design challenges. Before embarking on any renovation project, it's essential to have an accurate floor plan of the existing space. This will serve as a foundation for developing design ideas and communicating those ideas to contractors.
When planning interior design, a floor plan allows for experimenting with different furniture arrangements without physically moving heavy items. You can draw furniture to scale on the plan (or use digital tools) to test different layouts and see how they affect the flow of space. This can help avoid costly mistakes, such as purchasing furniture that's too large for the room or creating a layout that feels cramped and uncomfortable. Paying attention to circulation paths is also critical. A well-designed floor plan will facilitate smooth and comfortable movement through the space, connecting different areas in a logical and intuitive way.
For renovation projects, floor plans are essential for planning structural changes, such as moving walls or adding new rooms. A detailed floor plan will show the location of load-bearing walls, electrical wiring, and plumbing lines, which are all important factors to consider when planning renovations. This information helps to identify potential challenges and develop solutions to minimize disruption and ensure the structural integrity of the building. Before undertaking any structural alterations, it is crucial to consult with a qualified architect or structural engineer to ensure compliance with building codes and safety regulations. Local building codes dictate factors like egress window sizes, ceiling heights, and minimum room dimensions for habitable spaces.
Floor plans help to visualize the impact of proposed changes on the overall layout and functionality of the space. For example, opening up a wall between two rooms can create a more open and spacious feel, but it may also require relocating electrical outlets or plumbing fixtures. A floor plan allows you to explore these possibilities and plan the necessary modifications accordingly. Furthermore, floor plans contribute to obtaining accurate cost estimates from contractors. Detailed plans allow contractors to assess the scope of the project and provide more precise bids, reducing the likelihood of unexpected expenses down the line.
Key Element 3: Types of Floor Plans and Their Specific Applications
Different types of floor plans serve various purposes, ranging from basic layouts for real estate listings to highly detailed plans for construction and engineering. Understanding the different types of floor plans and their specific applications is crucial for choosing the appropriate plan for your needs.
Real estate floor plans are typically simplified diagrams that highlight the basic layout of the property, including the location of rooms, doors, and windows. These plans are used in marketing materials to give potential buyers a general overview of the property's structure and size. They usually include overall dimensions but may lack detailed information about fixtures, appliances, or electrical wiring. The focus is on presenting the space in an attractive and easy-to-understand manner to generate interest and encourage viewings.
Architectural floor plans are much more detailed and comprehensive. They are used by architects and builders to plan and execute construction projects. These plans include precise dimensions, specifications for materials, and details about structural elements, such as load-bearing walls, beams, and columns. They also indicate the location of electrical outlets, lighting fixtures, plumbing lines, and HVAC systems. Comprehensive architectural floor plans are necessary for obtaining building permits and ensuring compliance with building codes and regulations. These plans are often accompanied by elevations (drawings that show the exterior views of the building) and sections (drawings that show a cut-through view of the building).
Interior design floor plans focus on the layout of furniture, fixtures, and finishes. These plans are used by interior designers to create functional and aesthetically pleasing spaces. They typically include detailed information about furniture dimensions, materials, colors, and textures. They often incorporate lighting plans, showing the location and type of lighting fixtures, and electrical plans, indicating the placement of outlets and switches. These floor plans help to communicate design ideas to clients and guide the implementation of the design by contractors.
As-built floor plans represent the final built structure, reflecting any changes or modifications made during the construction process. These plans are crucial for future renovations or maintenance work. They provide an accurate record of the building's layout and infrastructure, which can be invaluable for troubleshooting problems or planning new additions. As-built plans are often required by local authorities after the completion of a construction project.
3D floor plans offer a more realistic and immersive way to visualize the space. They provide a three-dimensional representation of the building, allowing viewers to experience the spatial relationships and design elements in a more intuitive way. 3D floor plans are commonly used in real estate marketing and interior design presentations to give potential buyers or clients a better understanding of the property or design concept. They can be created using specialized software and often incorporate realistic textures, lighting, and furniture to enhance the visual experience.

Floor Plans Types Symbols Examples

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

Pin On House Layout

Where You Can Buy House Plans Live Home 3d

Love This Size House Plans Floor How To Plan

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

Floor Plan Creator And Designer Free Easy App

My Ideal House Floor Plan Plans Courtyard Simple

How To Read A Floor Plan With Dimensions Houseplans Blog Com

My Dream Home Free Design 3d Floor Plans By Planner 5d