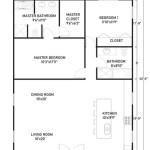
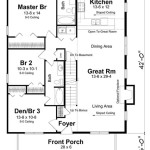
Energy Efficient House Plans For Cold Climates
Building an energy-efficient home in a cold climate requires careful consideration of several factors. These include building orientation, insulation, window selection, and heating systems. By integrating these elements effectively into the house plan, homeowners can significantly reduce energy consumption and create a comfortable living environment, even in the harshest winters.
Orientation plays a crucial role in passive solar gain, a key element in energy-efficient design. Ideally, the longest side of the house should face south to maximize exposure to sunlight during the day. This allows the sun to warm the interior spaces naturally, reducing the reliance on artificial heating systems. Large, south-facing windows can further enhance solar gain, while strategically placed overhangs can prevent overheating during the summer months.
Insulation is paramount in cold climates. A well-insulated house minimizes heat loss through the walls, roof, and foundation. This requires selecting insulation materials with high R-values, indicating their resistance to heat flow. Common insulation materials include fiberglass, cellulose, and spray foam. Ensuring adequate insulation thickness and proper installation is vital for achieving optimal energy efficiency.
Windows are a significant source of heat loss in any home. For cold climates, high-performance windows with low-E coatings are essential. These coatings minimize heat transfer while allowing natural light to enter. Multiple panes of glass create insulating air spaces, further reducing heat loss. Properly sealed frames and insulated window casings are crucial to prevent drafts and air leakage.
Airtight construction is a fundamental principle of energy-efficient building. Minimizing air leaks through cracks and gaps in the building envelope significantly reduces energy waste. This can be achieved through the use of air sealing techniques and materials, such as caulking, weather stripping, and spray foam insulation. A blower door test can identify air leaks and help pinpoint areas needing improvement.
Heating systems play a vital role in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures in cold climates. High-efficiency heating systems, such as heat pumps and geothermal systems, offer significant energy savings compared to traditional furnaces. Heat pumps extract heat from the outside air or ground and transfer it indoors, while geothermal systems utilize the stable temperature of the earth to provide heating and cooling.
Ventilation is essential for maintaining indoor air quality, even in energy-efficient homes. Proper ventilation systems, such as heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) and energy recovery ventilators (ERVs), can exchange stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air while minimizing heat loss. These systems use heat exchangers to transfer heat from the outgoing air to the incoming air, reducing the load on the heating system.
Building materials can also contribute to energy efficiency. Using locally sourced materials reduces transportation costs and associated emissions. Sustainable materials, such as recycled content insulation and reclaimed wood, minimize environmental impact. Structural insulated panels (SIPs) offer excellent insulation and airtightness, contributing to a highly energy-efficient building envelope.
Landscaping can play a supporting role in energy efficiency. Planting deciduous trees on the south side of the house provides shade during the summer months, while allowing sunlight to penetrate during the winter. Windbreaks, such as evergreen trees and shrubs, can reduce heat loss caused by wind exposure. Properly designed landscaping can create a microclimate around the house, further enhancing energy efficiency.
Beyond these core elements, incorporating smart home technology can optimize energy usage. Programmable thermostats allow homeowners to adjust heating and cooling schedules based on occupancy patterns, reducing energy waste when the house is unoccupied. Smart lighting systems can automatically adjust lighting levels based on ambient light and occupancy, further minimizing energy consumption.
Energy modeling software can be a valuable tool for designing energy-efficient homes. These tools simulate building performance under various climate conditions, allowing architects and builders to optimize design elements for maximum energy efficiency. Energy modeling can help predict energy consumption and identify potential areas for improvement during the design phase.
Choosing energy-efficient appliances and fixtures is another important consideration. Energy Star-rated appliances consume less energy than conventional models, leading to significant savings over time. Low-flow faucets and showerheads reduce water usage, which in turn reduces the energy required for water heating.
Regular maintenance is crucial for maintaining energy efficiency. This includes checking insulation for damage or settling, sealing air leaks, and regularly servicing heating and cooling systems. Proper maintenance ensures that all systems are operating at peak efficiency, minimizing energy waste.

Make Your Home More Energy Efficient The Jonah Center For Earth Art

Built For Energy Efficiency In A Cold Climate

Net Zero Energy Homes Pay Off Faster Than You Think Even In Chilly Midwest Inside Climate News

Net Zero House For A Cold Climate Jlc

Energy Efficient Home

15 Smart Design Choices For Cold Climates

Solar Pit House Plan

15 Smart Design Choices For Cold Climates

How To Build An Energy Efficient Home

Pin On Architecture Stuff