Canadian Home Plans and Designs: A Comprehensive Overview
The realm of Canadian home plans and designs is diverse, reflecting the nation's varied geography, climate, and cultural influences. Developing a residential building project requires careful consideration of numerous factors, extending from architectural styles to regional building codes. This article provides a detailed examination of key elements within the Canadian home building landscape.
Understanding the nuances of Canadian architecture necessitates a grasp of historical influences and modern adaptations. Early Canadian architecture was predominantly influenced by European styles, brought by settlers from France and Britain. These styles were subsequently modified to suit the Canadian environment and available materials. Contemporary Canadian home design embraces a mixture of influences, often incorporating sustainable practices and technological advancements.
Building a home involves a complex interplay of design, materials, and construction techniques. The selection of a suitable home plan is paramount, requiring careful evaluation of lifestyle needs, budget constraints, and site characteristics. A detailed understanding of architectural styles, construction processes, and regulatory compliance is essential for a successful project.
Key Considerations in Selecting Canadian Home Plans
Choosing the right home plan in Canada involves several critical factors. The first consideration is the size and layout of the home. This must correlate with the needs of the household, taking into account the number of occupants, their lifestyles, and anticipated future changes. Open-concept designs, for example, are popular for their spaciousness and social connectivity, while other homeowners may prefer a more traditional layout with defined rooms.
Budgetary constraints are also a significant determinant of home plan selection. The cost of construction varies dramatically based on size, materials, and complexity of the design. The final design must be tailored to fit within the allocated budget, with careful evaluation of potential cost-saving measures. This may include opting for simpler rooflines, using locally sourced materials, or choosing more efficient building techniques.
Site conditions play an important role in influencing the feasibility of certain home plans. The topography of the land, soil composition, and climate factors all impact the design and construction process. Sloping lots, for instance, may require specialized foundation designs, while regions with heavy snowfall necessitate robust roofing systems. Home plans must be adapted to the specific characteristics of the building site to ensure structural integrity and long-term durability.
Energy efficiency represents a growing priority in Canadian home design. The integration of energy-efficient features not only reduces long-term operating costs but also minimizes the environmental impact of the home. Passive solar design, high-performance windows, and advanced insulation materials are common strategies for enhancing energy efficiency. Understanding the principles of building science is essential for optimizing the thermal performance of the home.
Homeowners should also consider future resale value when selecting a home plan. Certain architectural styles and design features are more appealing to potential buyers, and may contribute to a higher resale price. Consulting with a real estate professional and researching local market trends can provide valuable insights into desirable design elements.
Popular Architectural Styles in Canada
Canadian architecture is characterized by a blend of historical influences and modern trends. The styles reflect the country's diverse cultural heritage and regional variations. Some of the most popular architectural styles in Canada include:
Victorian: This style is characterized by elaborate detailing, ornate trim, and asymmetrical designs. Victorian homes often feature steeply pitched roofs, bay windows, and decorative brackets. While these homes possess significant historical charm, they can require extensive maintenance and may not always be the most energy-efficient option.
Craftsman: Emphasizing natural materials and handcrafted details, the Craftsman style is known for its simple, clean lines and durable construction. These homes often feature low-pitched roofs, wide eaves, and exposed rafters. Craftsman homes are prized for their timeless appeal and comfortable living spaces.
Modern: Characterized by clean lines, minimalist aesthetics, and an emphasis on functionality, modern homes prioritize open spaces, large windows, and sustainable materials. Modern designs often incorporate passive solar heating and other energy-efficient features. The style can vary greatly, including mid-century modern, contemporary, and minimalist approaches.
Contemporary: This style is constantly evolving, reflecting current design trends and technological advancements. Contemporary homes often incorporate unique architectural features, unconventional materials, and innovative layouts. The style promotes energy efficiency and integration with the surrounding environment.
Farmhouse: Inspired by traditional rural architecture, farmhouse-style homes evoke a sense of warmth, comfort, and simplicity. These homes often feature gable roofs, large porches, and natural wood accents. Farmhouse designs often incorporate modern amenities while maintaining a rustic charm. More modern interpretations have opened to a more contemporary style known as "Modern Farmhouse," which is growing in popularity in Canada.
Bungalow: Typically single-story or story-and-a-half homes with a low-pitched roof, bungalows are a common and practical style in Canada. Often they feature open-concept living spaces and a focus on functionality and affordability. They are generally easy to maintain and well-suited for various climates.
The choice of architectural style is highly personal and should reflect the homeowner's preferences, lifestyle, and budget. It is also essential to consider the surrounding neighborhood and local architectural guidelines to ensure that the new home complements the existing community.
Navigating Building Codes and Regulations in Canada
Construction in Canada is governed by a comprehensive set of building codes and regulations designed to ensure the safety, durability, and energy efficiency of homes. These codes vary by province and municipality, requiring homeowners to be well-versed in local requirements.
The National Building Code of Canada (NBC) serves as a model code for the provinces and territories, outlining minimum standards for structural integrity, fire safety, and accessibility. Each province and territory adapts the NBC to reflect local conditions and priorities, introducing regional variations. Municipalities may also have additional bylaws regulating zoning, setbacks, and architectural design.
Obtaining the necessary building permits is a crucial step in the construction process. Permit requirements vary depending on the scope of the project and the location of the property. Homeowners must submit detailed plans and specifications to the local building department for review and approval. The permitting process ensures that the proposed construction complies with all applicable codes and regulations.
Inspections are conducted throughout the construction process to verify compliance with the approved plans and building codes. These inspections typically cover aspects such as foundation construction, framing, plumbing, electrical, and mechanical systems. Addressing any deficiencies identified during inspections is critical for obtaining final occupancy approval.
Energy efficiency requirements are increasingly stringent in Canadian building codes. The Model National Energy Code for Buildings (MNECB) outlines minimum energy performance standards for new construction. Provinces are adopting and adapting the MNECB to promote energy conservation and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Compliance with energy efficiency requirements may involve installing high-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows, and advanced heating and cooling systems.
Accessibility is another key consideration in Canadian building codes. Regulations such as the Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act (AODA) in Ontario require new construction to be accessible to people with disabilities. These regulations may include requirements for ramps, wider doorways, and accessible bathrooms. Incorporating accessibility features into the home design can improve the quality of life for individuals with disabilities and enhance the overall usability of the home.
Navigating the complexities of Canadian building codes and regulations can be challenging. Engaging with experienced architects, builders, and building code consultants is often advisable. These professionals can provide guidance on compliance requirements, assist with the permitting process, and ensure that the new home meets all applicable standards.
Ultimately, successful Canadian home plans and designs demand a thorough understanding of architectural styles, regional conditions, and regulatory frameworks. By carefully considering these factors, homeowners can create functional, aesthetically pleasing, and sustainable living spaces that cater to their unique needs and preferences.

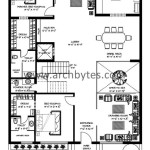
Canadian House Plans Home Floor Designs The Designers

Top 100 Most Popular Canadian House Plans Drummond

Top 100 Most Popular Canadian House Plans Drummond

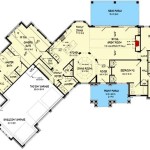
Canadian House Plans Home Floor Designs The Designers

Top 100 Most Popular Canadian House Plans Drummond

Top 100 Most Popular Canadian House Plans Drummond

Canadian House Plans Home Floor Designs The Designers

Country Style House Plan 6344 Canadian

House The Canadian Plan Green Builder Plans

Canadian House Plans Edesignsplans Ca